Our company has a reputation for superior products, customer service, and dependability. All our fastener products are built to last, and we know that our customers appreciate our dedication to using the best materials and manufacturing techniques. If you would like to learn more about us, contact us by phone or email, or stop by our website today!

With more than 130,000 commercial and industrial grade fasteners in inventory, our wide distribution network is positioned to get you the parts you need fast. Whether we’re keeping your bins full with a Vendor Managed Inventory Program or rushing emergency replacement parts with 24-hour on-call service, you’ll know that we’ve got you covered. Our HQ’s quality system is certified to AS9120 ...

At DW Fastener, we take pride in our extensive range of fasteners designed to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. Industrial fasteners play a crucial role in securely joining various surfaces or objects together in a wide array of applications, and we understand their significance in ensuring the reliability and integrity of your projects.

Blue Ribbon Fastener (BRF) supplies North American OEMs with high-quality fasteners and industrial hardware. Founded in 1985, BRF offers decades of experience and a diverse network of both domestic and international suppliers.

At Warmington Industries, we have built our reputation as a trusted manufacturer and supplier of precision fasteners that support a wide range of industries. We specialize in delivering fastening solutions that meet the exacting demands of construction, manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and countless other applications where strength, reliability, and consistency are critical.

P&R is a manufacturer of industrial fasteners, specialty fasteners, automotive fasteners, stainless steel fasteners, aerospace and electronic fasteners. We provide over 60 years of experience in designing quality industrial fastener products. Give us a call so we can work together.

Delta Fastener Corp. supplies headed fasteners from only quality manufacturers. Our huge, readily available selection includes industrial bolts, nuts, washers, screws, etc. in a wide range of metal types and grades. Check out our online catalog or give us a call today for industrial bolts and more!

As a fastener manufacturer, Chicago Nut & Bolt wants you to know that your standard fasteners or special fastener in extra-large and extra-long sizes are not a cause for concern. We are used to working with 1/4"-3" diameters and lengths up to 72". Try us for your next needs.

More Stainless Steel Fastener Manufacturers
Stainless steel fasteners are essential components in a vast range of industries, offering superior corrosion resistance and remarkable durability. These fasteners are made from stainless steels—a specialized class of iron-based alloys containing at least 12% chromium. The presence of chromium is what gives stainless steel its defining ability to resist corrosion, as it forms a thin, invisible, and self-healing layer of chromium oxide when exposed to oxygen. This passive film plays a critical role in protecting stainless steel from oxidation and rust, setting it apart from standard steel fasteners.
In addition to chromium, stainless steels often contain elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and sometimes titanium or nitrogen. These alloying elements further enhance corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and toughness, making stainless steel fasteners ideal for demanding environments where reliability and longevity are crucial. Industries such as construction, automotive, marine, chemical processing, food production, and aerospace frequently rely on stainless steel bolts, screws, nuts, washers, and other fastener types to ensure structural integrity and long-term performance.
Are you searching for the right stainless steel fasteners for your specific application? Do you need advice on material selection, grades, or sourcing quality fastener suppliers? This comprehensive guide will help you understand the different types, grades, manufacturing methods, applications, and key decision factors when choosing stainless steel fasteners for your next project.
Two Most Common Stainless-Steel Fastener Alloys: 304 vs. 316
Among the various grades of stainless steel, SAE 304 stainless steel and SAE 316 stainless steel are by far the most widely used alloys for manufacturing fasteners. These alloys belong to the austenitic 300 series and are favored for their excellent combination of corrosion resistance, strength, and workability. Understanding the differences between these two alloys can help you select the optimal fastener for your environment and application requirements.
- SAE 304 Stainless Steel Fasteners: Often referred to as 18-8 stainless steel, 304 contains approximately 18–20% chromium and 8–12% nickel. This grade is highly versatile and is commonly used in general-purpose applications that require good corrosion resistance. Typical uses include kitchen equipment, food processing machinery, architectural structures, automotive components, piping systems, and household appliances. 304 stainless steel fasteners are resistant to oxidation in a wide variety of atmospheric environments and many corrosive media.
- SAE 316 Stainless Steel Fasteners: Known as “marine grade” stainless steel, 316 contains 16–18% chromium, 10–14% nickel, and 2–3% molybdenum. The addition of molybdenum significantly enhances resistance to chlorides, saltwater, and harsh chemicals, making 316 fasteners the top choice for marine hardware, boat construction, chemical processing plants, medical devices, and outdoor installations exposed to de-icing salts or seawater. 316 fasteners are especially valued for their performance in highly corrosive environments.


How Do 304 and 316 Stainless Steel Fasteners Differ?
When evaluating which stainless steel fastener grade is best for your project, consider the following:
- Corrosion Resistance: 316 stainless fasteners outperform 304 in environments with high chloride exposure, such as coastal structures, swimming pools, and chemical processing plants.
- Strength and Mechanical Properties: Both grades exhibit similar mechanical strengths, but 316 may offer slightly better resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion under aggressive conditions.
- Cost Considerations: 316 fasteners are typically more expensive due to the addition of molybdenum, but their enhanced durability can result in long-term savings by reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
- Applications: 304 is suitable for most indoor and mildly corrosive outdoor environments, while 316 is recommended for marine, medical, or highly corrosive applications.
Not sure which grade you need? Ask yourself: Will my fasteners be exposed to saltwater, chemicals, or extreme weather? Is long-term durability in a harsh environment a top priority? If so, 316 may be your best choice for optimal corrosion protection.
Manufacturing Processes for Stainless-Steel Fasteners
The manufacturing of stainless steel fasteners involves precise and specialized techniques to ensure high strength, optimal performance, and consistent quality. There are two primary methods used to produce these fasteners—cold heading (cold forming) and machining—each offering unique advantages depending on production volumes and application needs.
Cold Heading (Cold Forming)
Cold heading is a highly efficient process used for the mass production of stainless steel fasteners such as bolts, screws, and rivets. In this technique, stainless steel wire is fed through a series of dies and punches to form the desired shape without heating the material. Cold heading improves the fastener’s grain structure, leading to enhanced mechanical properties, increased tensile strength, and greater fatigue resistance. This method is ideal for producing large quantities of small- to medium-sized fasteners that require uniformity and cost-effectiveness.

Machining
Machining is a subtractive manufacturing process involving the use of lathes, mills, drills, or CNC machines to cut and shape stainless steel into the final fastener form. This method is typically used for custom fasteners, specialty bolts, or low-volume production runs where complex geometries or larger sizes are required. While machining offers flexibility and precision, it can be more expensive and may result in slightly lower fatigue resistance compared to cold-formed fasteners.

Thread Rolling and Secondary Processes
After the initial shaping, threads are typically rolled onto the fastener using dies or formed during machining. Thread rolling increases surface hardness and enhances the fatigue life of the fastener. Additional processes, such as heat treatment, passivation, and surface finishing (polishing, coating, or plating), may be applied to further improve corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and mechanical performance. For even greater strength, precipitation hardening—a specialized aging process—may be used to create high-strength stainless steel fasteners for critical structural and aerospace applications.
Benefits and Advantages of Stainless-Steel Fasteners
1. Unmatched Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Stainless steel fasteners are renowned for their ability to resist rust, tarnishing, and surface degradation even in challenging environments. The passive chromium oxide layer protects the fastener from moisture, chemicals, and atmospheric conditions, ensuring a long service life. This makes stainless steel the ideal choice for outdoor construction, marine hardware, food processing, and environments where hygiene and cleanliness are essential.
2. High Strength, Toughness, and Load Capacity
Engineered to withstand high tension, shear, and cyclic loading, stainless steel fasteners offer superior strength and ductility compared to many other fastener materials. They maintain their integrity under heavy loads, vibration, and dynamic stresses, making them suitable for structural, automotive, and industrial applications.
3. Versatile Applications Across Industries
Stainless steel fasteners are used in a multitude of sectors, including:
- Construction & Infrastructure: Bridges, buildings, railings, facades, and roofing systems.
- Automotive & Transportation: Engine components, exhaust systems, and chassis assemblies.
- Marine & Offshore: Boat hardware, docks, oil platforms, and coastal structures.
- Food & Beverage Processing: Equipment, conveyors, and sanitary fittings.
- Medical Devices: Surgical instruments, implants, and hospital equipment.
- Electronics: Enclosures, mounting hardware, and circuit board assemblies.
- Renewable Energy: Wind turbines, solar panel mounts, and hydroelectric installations.
4. Cost-Effectiveness and Low Maintenance
While the initial cost of stainless steel fasteners may be higher than carbon steel or zinc-plated alternatives, their superior durability, reduced maintenance requirements, and long lifespan result in a lower total cost of ownership. Over time, you save on repairs, replacements, and downtime, making stainless steel an economically smart choice for critical infrastructure and high-value assets.
5. Attractive Appearance and Design Flexibility
The natural luster and smooth finish of stainless steel fasteners make them an aesthetically pleasing option for exposed applications, architectural designs, and consumer products. They are available in a variety of finishes, such as brushed, polished, or matte, and can be easily cleaned for a consistently attractive appearance. This makes them ideal for visible installations, luxury goods, and products where design matters as much as function.
6. Environmentally Sustainable and Recyclable
Stainless steel is a 100% recyclable material. At the end of their service life, stainless steel fasteners can be fully recycled to recover valuable alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. By choosing stainless steel, you contribute to resource conservation, reduced landfill waste, energy savings, and lower CO2 emissions—making these fasteners a green and sustainable choice for environmentally conscious projects.
7. Ease of Installation and Removal
Stainless steel fasteners are designed for quick and simple assembly or disassembly. Standard tools such as wrenches and screwdrivers are typically all that’s needed to install or remove them. This ease of use is particularly beneficial in maintenance-intensive settings, field repairs, and modular construction projects.
Types of Stainless Steel Fasteners: What Are Your Options?
Stainless steel fasteners come in a wide range of types, sizes, and configurations—each designed to meet specific functional and performance requirements. Here are some of the most common categories:
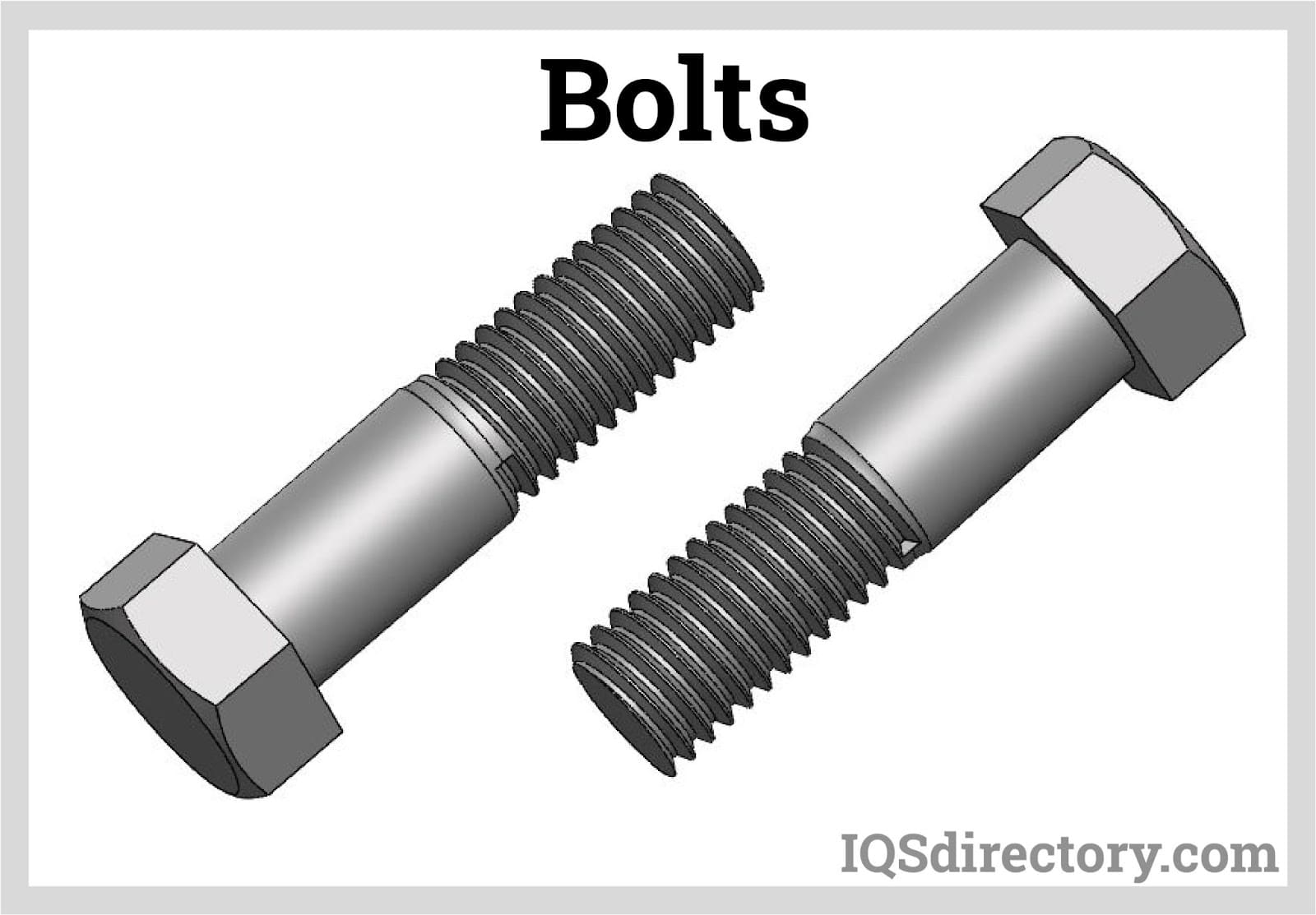
- Stainless Steel Bolts: Available in hex head, carriage, flange, and anchor configurations for structural connections.
- Stainless Steel Screws: Includes machine screws, self-tapping screws, wood screws, and sheet metal screws for joining materials in construction, woodworking, and electronics.
- Stainless Steel Nuts: Hex nuts, lock nuts, wing nuts, and cap nuts used in conjunction with bolts and threaded rods.
- Stainless Steel Washers: Flat washers, lock washers, and fender washers for load distribution and vibration resistance.
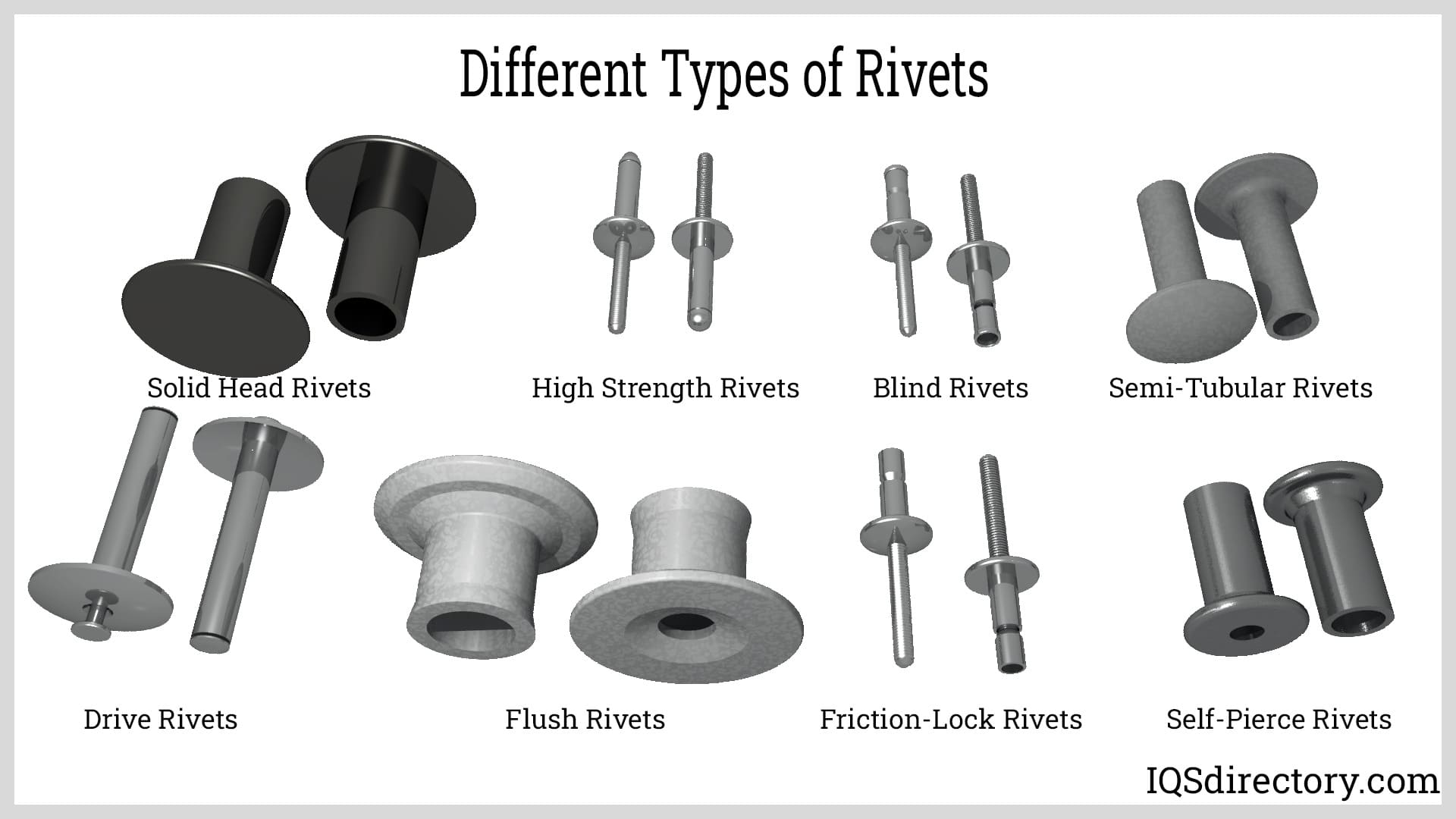
- Stainless Steel Rivets: Blind, solid, and pop rivets for permanent, tamper-resistant fastening.
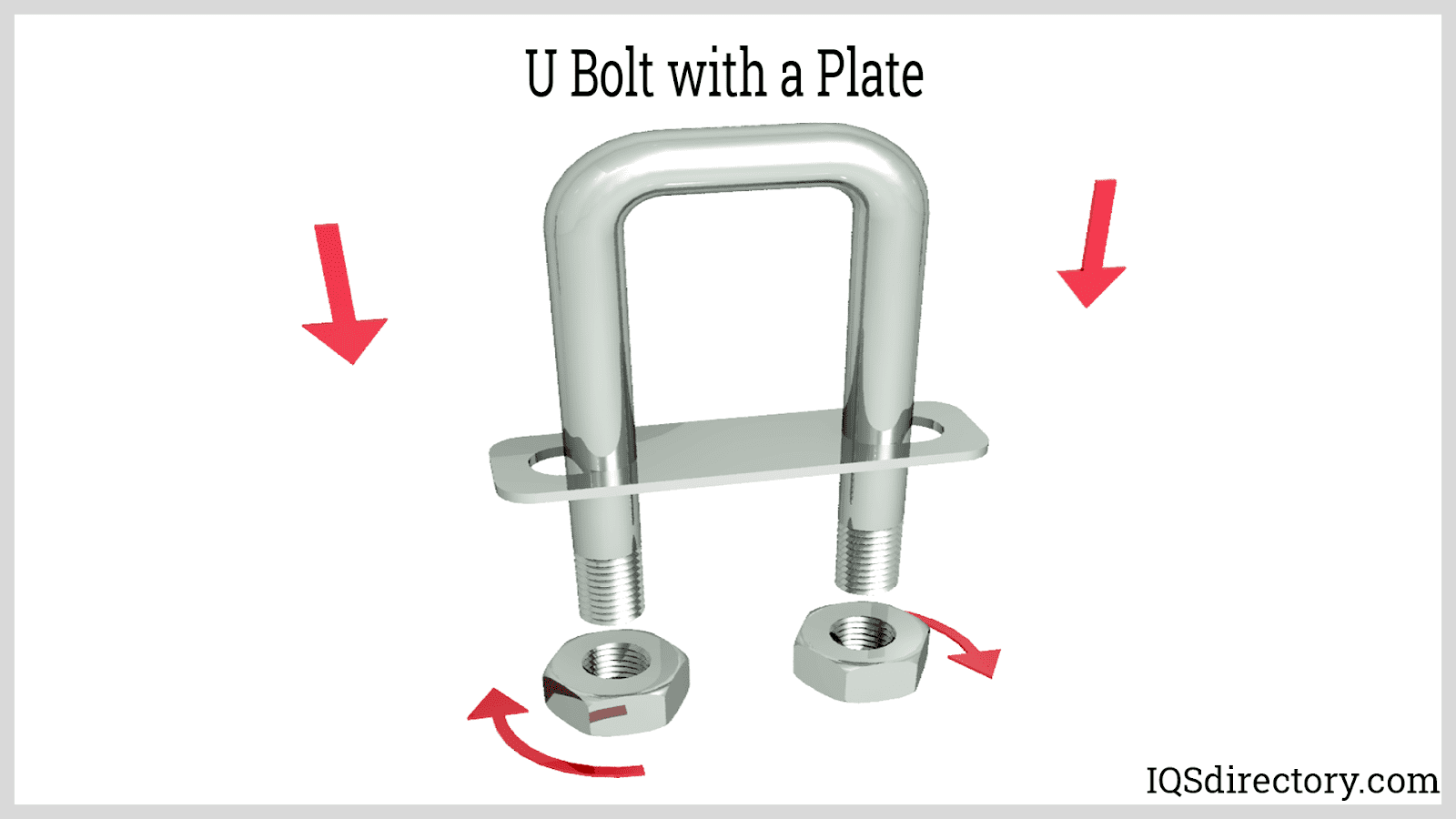
- Stainless Steel Anchors: Wedge anchors, sleeve anchors, and drop-in anchors for secure attachment to masonry or concrete.
Looking for a specific type of fastener for your industry or project? Explore our directory of stainless steel fastener manufacturers for detailed product listings and technical specifications.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Stainless Steel Fasteners
1. Selecting the Appropriate Grade: 304, 316, or Specialty Alloys
Your choice of stainless steel grade should be guided by the environmental conditions and performance demands of your application. For most indoor and mildly corrosive environments, 304 stainless steel fasteners offer reliable performance at a competitive price. For marine, chemical, or outdoor settings exposed to de-icing salts, 316 stainless steel is strongly recommended due to its superior resistance to chlorides and aggressive chemicals. Specialty grades, such as 410 (martensitic, for high strength and wear resistance) or duplex stainless steels (for combined strength and corrosion resistance), may be suitable for niche requirements.
2. Surface Finish and Coatings
Stainless steel fasteners are available with various finishes, including passivated, polished, or coated options. A polished finish provides an extra layer of corrosion resistance and is ideal for architectural or exposed applications. Passivation removes surface contaminants and enhances the protective oxide film, further improving longevity. For extreme environments, additional coatings (such as PTFE or Xylan) may be applied for added chemical or temperature resistance.
3. Mechanical Properties and Load Ratings
Consider the required tensile strength, shear strength, and fatigue resistance for your application. Consult technical datasheets or engineering standards to ensure your selected fastener meets the necessary performance criteria. For high-stress or safety-critical applications, choose fasteners certified to industry standards such as ASTM, ISO, or DIN.
4. Size, Thread Type, and Compatibility
Ensure that the fastener dimensions, thread pitch (coarse or fine), and compatibility with mating components align with your assembly requirements. Custom sizes and thread types are available from specialized manufacturers for unique or challenging applications.
5. Compliance, Certification, and Traceability
For regulated industries (such as aerospace, medical, or food processing), verify that your stainless steel fasteners are supplied with the necessary certifications (e.g., material certificates, RoHS, REACH) and traceability documentation. This ensures compliance with industry standards and quality requirements.
6. Supplier Reliability and Support
Choosing a trusted and experienced stainless steel fastener supplier is critical to ensuring consistent product quality, timely delivery, and technical support. Look for suppliers with a proven track record, broad product range, and comprehensive customer service capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions: Stainless Steel Fasteners
- What is the difference between stainless steel and galvanized fasteners?
Stainless steel fasteners are inherently corrosion-resistant due to their alloy composition, while galvanized fasteners have a zinc coating that can wear off over time. Stainless steel is generally preferred for harsh or long-term outdoor applications. - Can I use stainless steel fasteners with aluminum components?
Yes, but use insulating washers or coatings to prevent galvanic corrosion between dissimilar metals, especially in wet or saline environments. - Are stainless steel fasteners magnetic?
Most austenitic stainless steels (such as 304 and 316) are non-magnetic in the annealed condition, but may become slightly magnetic after cold working or machining. - How do I identify the correct stainless steel grade?
Check product markings, supplier documentation, or request a material test report. Consult with your supplier or engineer if in doubt. - Where can I buy stainless steel fasteners in bulk?
Use our directory of stainless steel fastener suppliers to compare manufacturers, request quotes, and review technical capabilities.
Applications and Use Cases for Stainless Steel Fasteners
Stainless steel fasteners are found in countless applications where durability, safety, and appearance are vital. Some common use cases include:
- Outdoor Furniture and Landscaping: Decking, pergolas, fencing, and playground equipment require fasteners that resist corrosion and maintain appearance in all weather conditions.
- Food Processing and Commercial Kitchens: Fasteners must withstand frequent washdowns, cleaning agents, and exposure to food acids without contaminating products or corroding.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical Equipment: Sterilization, hygiene, and resistance to harsh cleaning chemicals are paramount.
- Marine Construction: Docks, piers, and boat fittings need fasteners that resist salt spray and prevent structural failure.
- Renewable Energy Installations: Wind turbines and solar panels rely on corrosion-resistant fasteners for long-term performance in outdoor environments.
- Heavy Industry and Oil & Gas: Chemical plants, refineries, and offshore platforms utilize stainless steel fasteners to withstand aggressive chemicals and extreme temperatures.
Are you planning a project in one of these industries? Contact our recommended stainless steel fastener suppliers for expert guidance and product recommendations tailored to your needs.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Fastener Supplier
To ensure the most beneficial outcome when purchasing stainless steel fasteners from a stainless steel fastener supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of stainless steel fastener suppliers. Each stainless steel fastener supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each stainless steel fastener business website using our patented website previewer to quickly learn what each business specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple stainless steel fastener companies with the same form.
Ready to get started? Browse our directory to compare stainless steel fastener manufacturers, request quotes, and find the perfect supplier for your industry or application.
Conclusion: Why Choose Stainless Steel Fasteners?
Stainless steel fasteners deliver unparalleled performance, reliability, and longevity in a host of applications and industries. By understanding the different grades, manufacturing methods, and selection criteria, you can make informed decisions that ensure optimal results for your next project. Whether you need corrosion-resistant bolts for marine construction, hygienic screws for food processing, or high-strength anchors for structural steelwork, stainless steel offers a proven, sustainable, and cost-effective solution.
Still have questions? Contact our experts or explore our in-depth guides for more information on stainless steel fastener types, grades, and sourcing tips. Invest in quality—choose stainless steel fasteners for your most demanding applications.
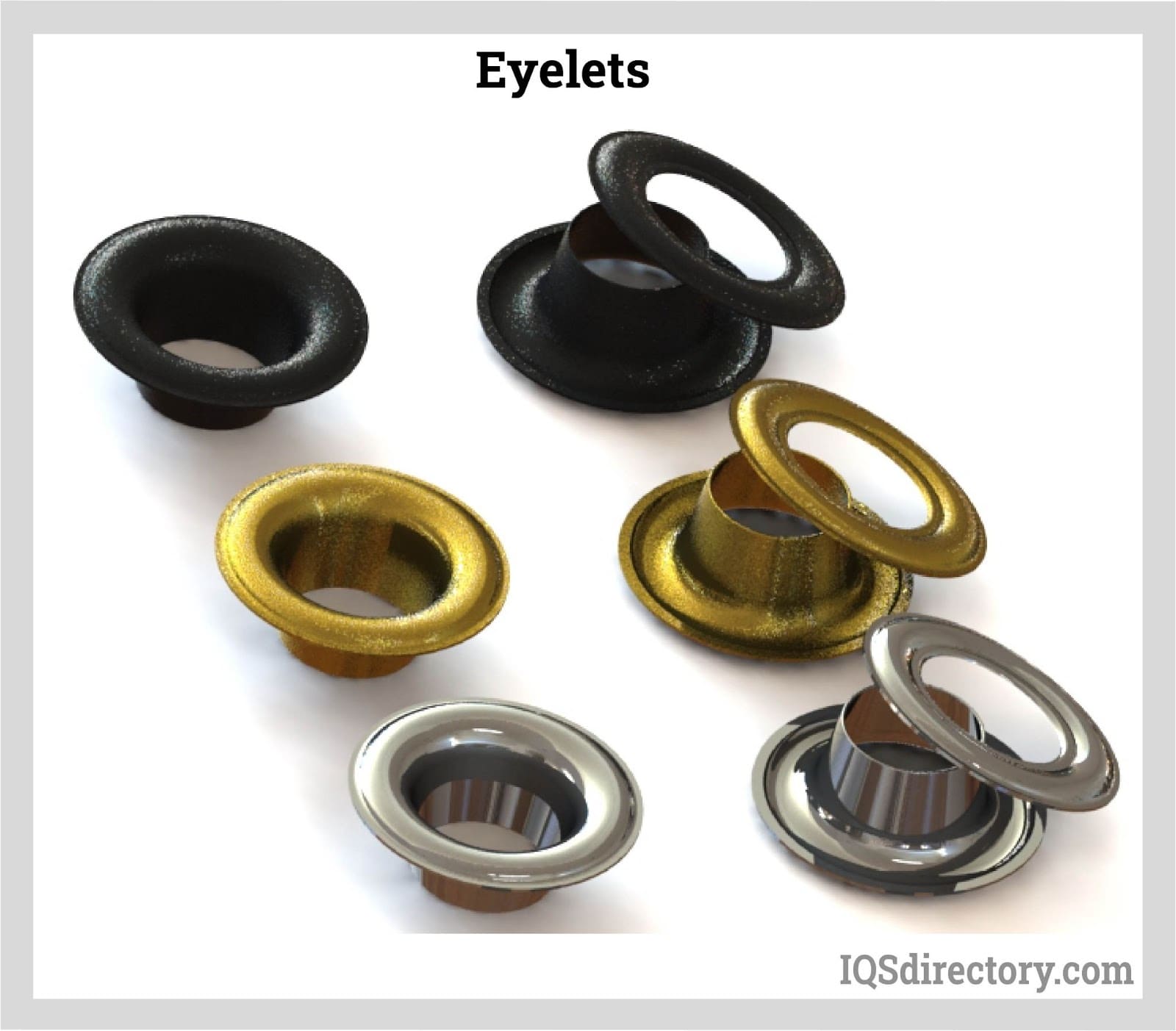








 Bolts
Bolts Fasteners
Fasteners Gas Spring
Gas Spring Handles
Handles Hinges
Hinges Latches
Latches Locks
Locks WIre Hooks
WIre Hooks Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services