Our company has a reputation for superior products, customer service, and dependability. All our fastener products are built to last, and we know that our customers appreciate our dedication to using the best materials and manufacturing techniques. If you would like to learn more about us, contact us by phone or email, or stop by our website today!

With more than 130,000 commercial and industrial grade fasteners in inventory, our wide distribution network is positioned to get you the parts you need fast. Whether we’re keeping your bins full with a Vendor Managed Inventory Program or rushing emergency replacement parts with 24-hour on-call service, you’ll know that we’ve got you covered. Our HQ’s quality system is certified to AS9120 ...

At DW Fastener, we take pride in our extensive range of fasteners designed to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. Industrial fasteners play a crucial role in securely joining various surfaces or objects together in a wide array of applications, and we understand their significance in ensuring the reliability and integrity of your projects.

Blue Ribbon Fastener (BRF) supplies North American OEMs with high-quality fasteners and industrial hardware. Founded in 1985, BRF offers decades of experience and a diverse network of both domestic and international suppliers.

At Warmington Industries, we have built our reputation as a trusted manufacturer and supplier of precision fasteners that support a wide range of industries. We specialize in delivering fastening solutions that meet the exacting demands of construction, manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and countless other applications where strength, reliability, and consistency are critical.

P&R is a manufacturer of industrial fasteners, specialty fasteners, automotive fasteners, stainless steel fasteners, aerospace and electronic fasteners. We provide over 60 years of experience in designing quality industrial fastener products. Give us a call so we can work together.

Delta Fastener Corp. supplies headed fasteners from only quality manufacturers. Our huge, readily available selection includes industrial bolts, nuts, washers, screws, etc. in a wide range of metal types and grades. Check out our online catalog or give us a call today for industrial bolts and more!

As a fastener manufacturer, Chicago Nut & Bolt wants you to know that your standard fasteners or special fastener in extra-large and extra-long sizes are not a cause for concern. We are used to working with 1/4"-3" diameters and lengths up to 72". Try us for your next needs.

More Industrial Fastener Manufacturers
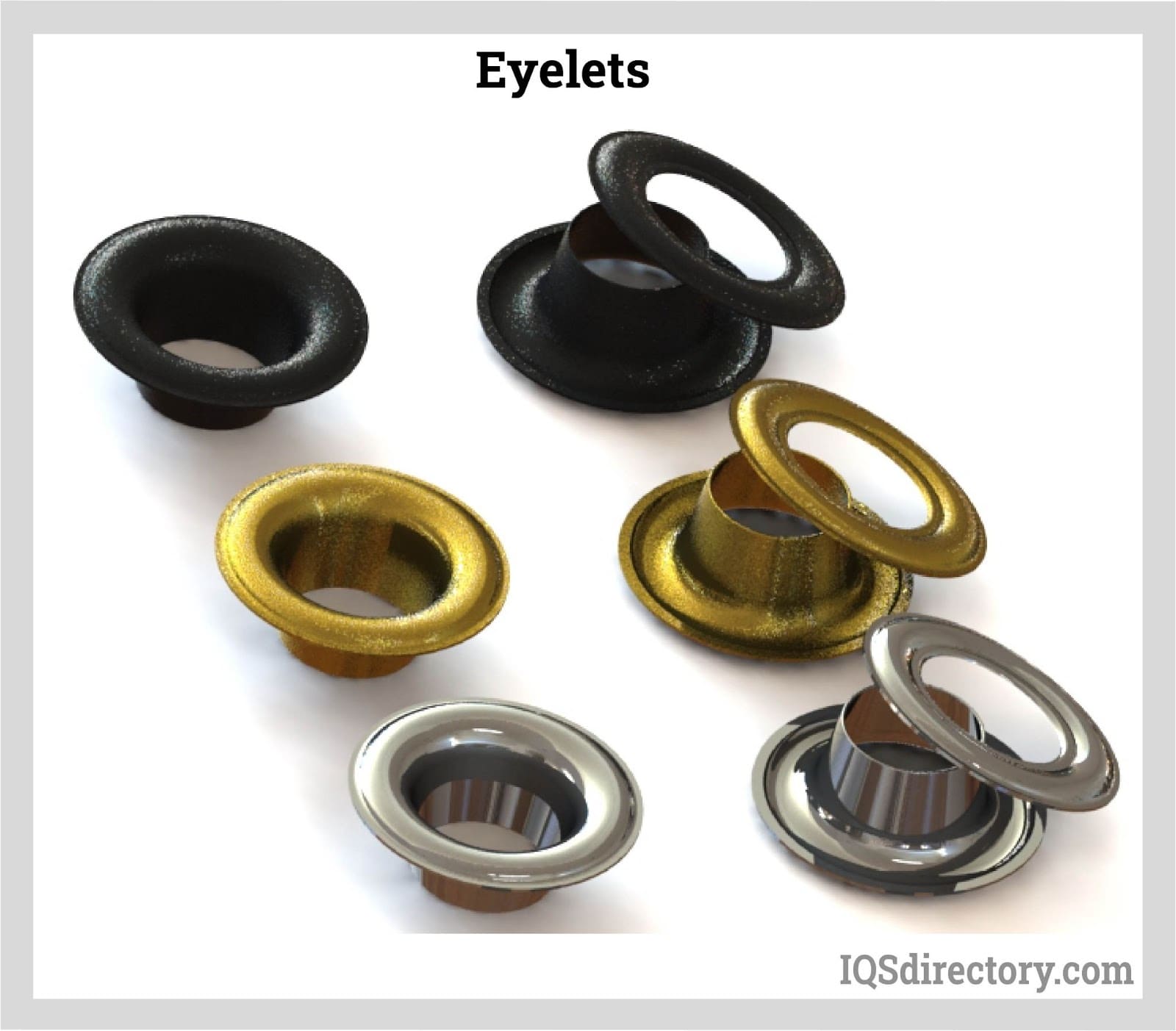
Industrial fasteners are a large and essential group of mechanical devices engineered to permanently or semi-permanently join two or more components. These critical hardware elements include nuts, bolts, hinges, studs, handles, knobs, flanges, rivets, and screws. Fasteners play a pivotal role in virtually every industry, supporting the assembly and structural integrity of everything from heavy industrial equipment, electric motors, and robotics to consumer goods such as smartphones and household appliances. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable in manufacturing, construction, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and countless other sectors.
Types of Industrial Fasteners
The world of industrial fasteners is vast, encompassing a diverse range of shapes, sizes, materials, and mechanical properties. Whether you are an engineer searching for a solution to a specific load-bearing challenge or a procurement specialist evaluating suppliers, understanding the different types of fasteners—and their ideal use cases—is fundamental for successful assembly, increased product lifespan, and safety compliance.
Fasteners are commonly categorized by their physical structure (such as threaded or non-threaded) and by their intended permanence (permanent vs. non-permanent). These classifications help engineers and buyers match fasteners to the mechanical, environmental, and economic requirements of their applications.
Threaded Fasteners
Threaded fasteners feature helical ridges (threads) that allow them to be screwed into pre-tapped holes or paired with internally threaded components like nuts. This design enables secure, adjustable, and often removable connections. Some of the most common threaded fasteners include:
Screws
Screws are among the most versatile and widely used industrial fasteners. Featuring a threaded shaft, they are designed to be driven into materials by rotational force, typically without requiring a nut. Their exceptional gripping power makes them ideal for wood, metal, plastic, and composite assemblies. Screws come in various subtypes tailored for distinct applications:
- Machine screws: Used in machinery, electronics, and automotive assemblies; paired with tapped holes or nuts.
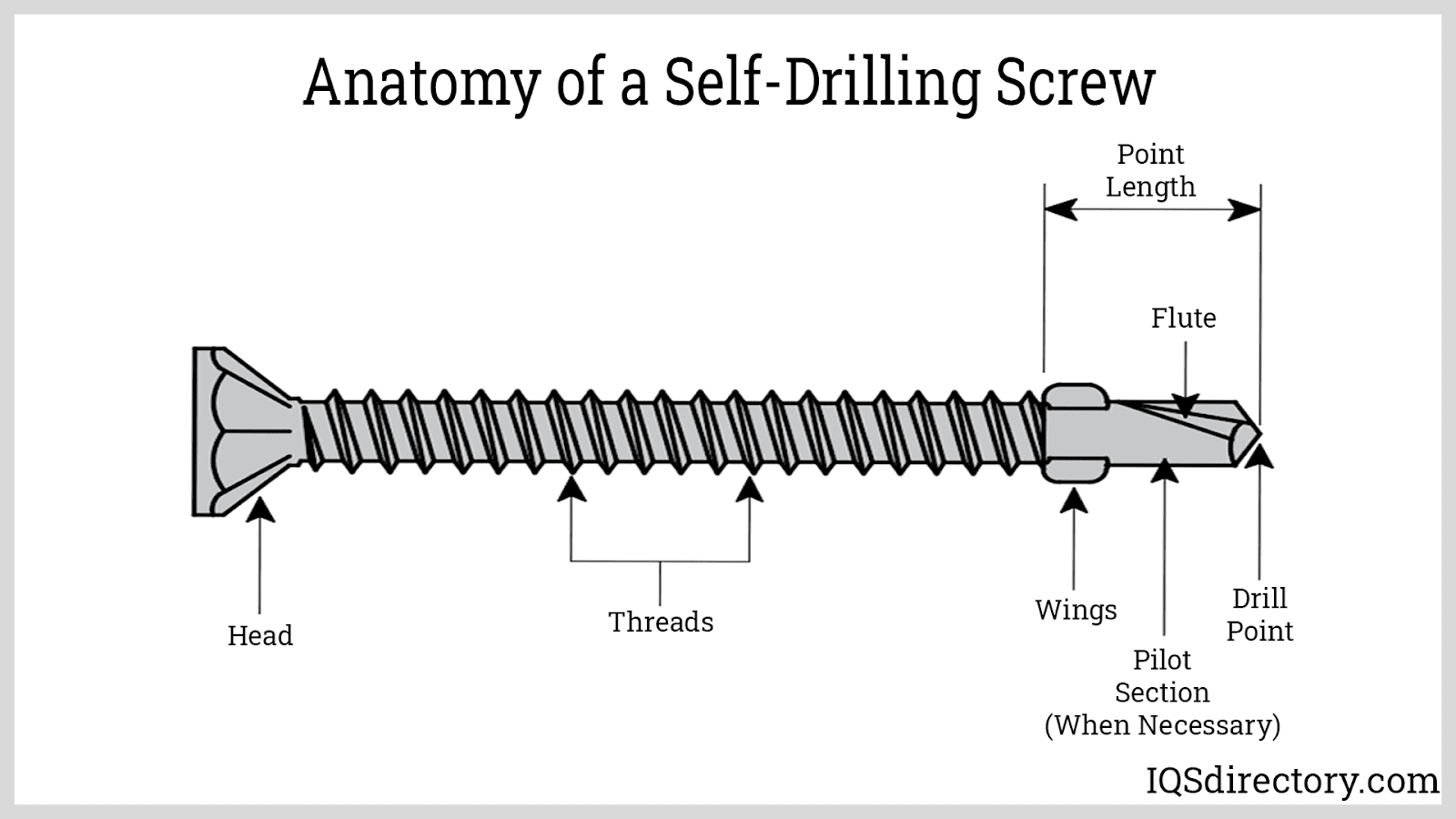
- Self-drilling screws: Incorporate a drill-like tip for fastening metal sheets without pre-drilling.
- Thumbscrews: Designed for tool-free hand tightening, often used in enclosures and panels.
- Shoulder screws: Feature a smooth cylindrical section for pivoting applications.
- Wood screws: Optimized for joining timber and wood-based materials.

Choosing the right screw type is crucial for ensuring optimal holding strength, corrosion resistance, and ease of assembly. Are you unsure which screw best fits your material or environment? Explore our screw manufacturer directory for expert guidance on application-specific solutions.
Nuts
Nuts are internally threaded fasteners designed to mate with bolts or threaded rods. They come in a variety of types, each offering unique benefits for strength, locking ability, vibration resistance, and specific installation environments. Common nut types include:
- Hex nuts: The most widely used, ideal for general-purpose fastening in construction and machinery.
- Lock nuts: Engineered to resist loosening under vibration and dynamic loads.
- Wing nuts: Feature tabs for hand tightening in tool-free applications.
- Flange nuts: Incorporate a broad flange to distribute load and minimize damage to the assembly surface.
- Cap nuts: Cover exposed bolt ends to protect threads and improve safety.
Comparing nut types? Browse leading nut manufacturers and request information on custom or bulk orders.
Bolt Fasteners
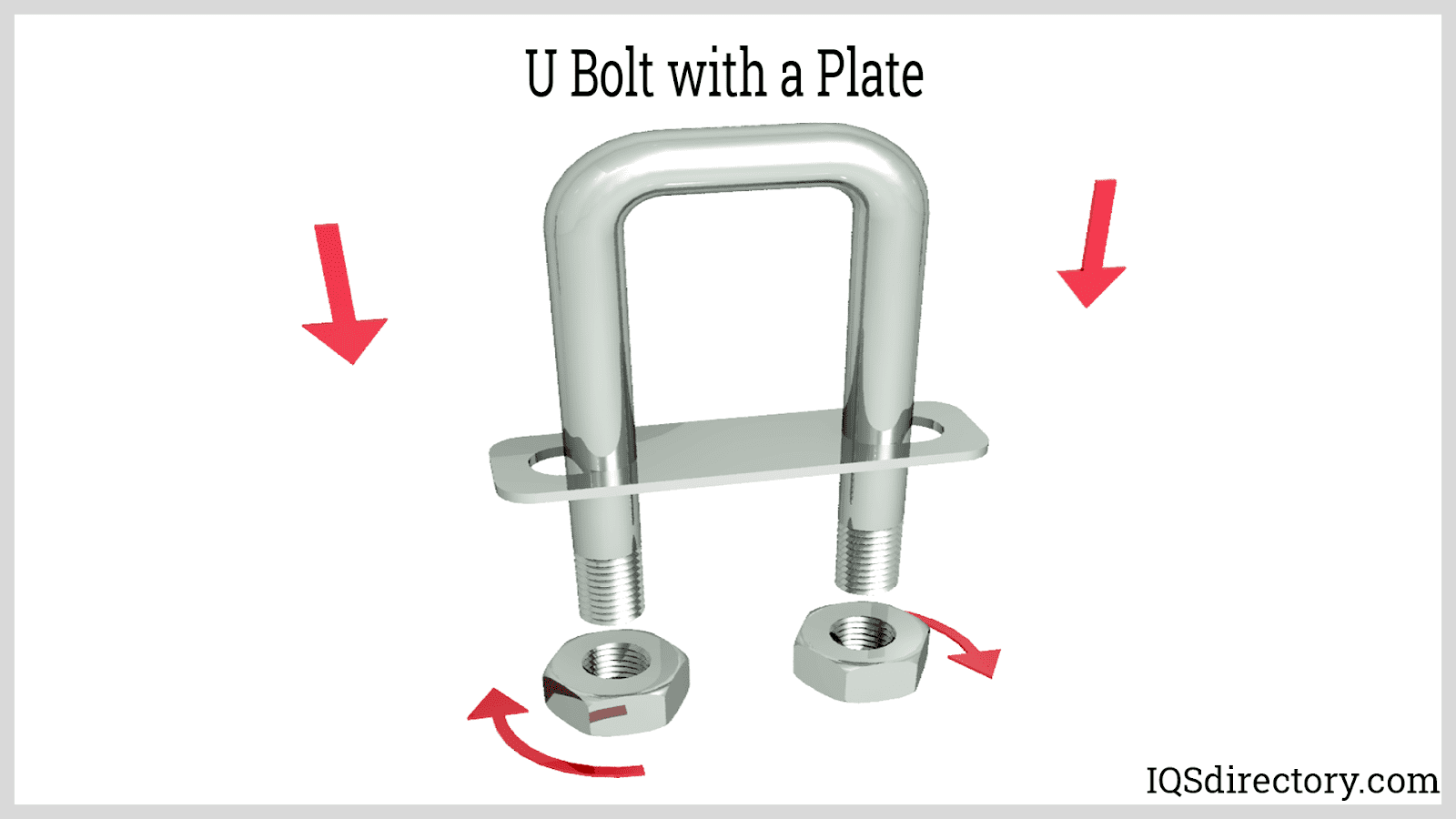
Bolt fasteners are externally threaded fasteners used in conjunction with nuts or pre-tapped holes to clamp components together. Bolts are typically stronger than screws and are favored in structural, heavy-duty, and load-bearing applications. Key bolt varieties include:
- Hex bolts: Standard for construction, machinery, and automotive assemblies.
- Carriage bolts: Feature a smooth, rounded head and square neck to prevent rotation during tightening—ideal for wood-to-metal or wood-to-wood connections.
- Lag bolts (lag screws): Heavy-duty fasteners for anchoring wood or other materials to masonry.
- Anchor bolts: Used to secure structures to concrete foundations.

Need help selecting the best bolt for your application? Connect with top bolt manufacturers for expert assistance and custom solutions.
Non-Threaded Fasteners
Non-threaded fasteners provide mechanical joining without threads. They are often used when permanent or semi-permanent assembly is required, or when vibration and shear resistance are priorities. Common non-threaded fastener types include:
- Pins: Dowel, cotter, and spring pins for precise alignment and securing moving parts.
- Keys: Transmit torque between shafts and hubs in power transmission assemblies.
- Retaining rings: Snap into grooves to hold components in place on shafts or in bores.
- Clips and clamps: Secure hoses, cables, or panels in place.
- Rivets: Provide high-strength, tamper-resistant permanent joints.
Non-threaded fasteners are crucial in industries where vibration, shock, and tampering must be minimized, such as aerospace, rail, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery.
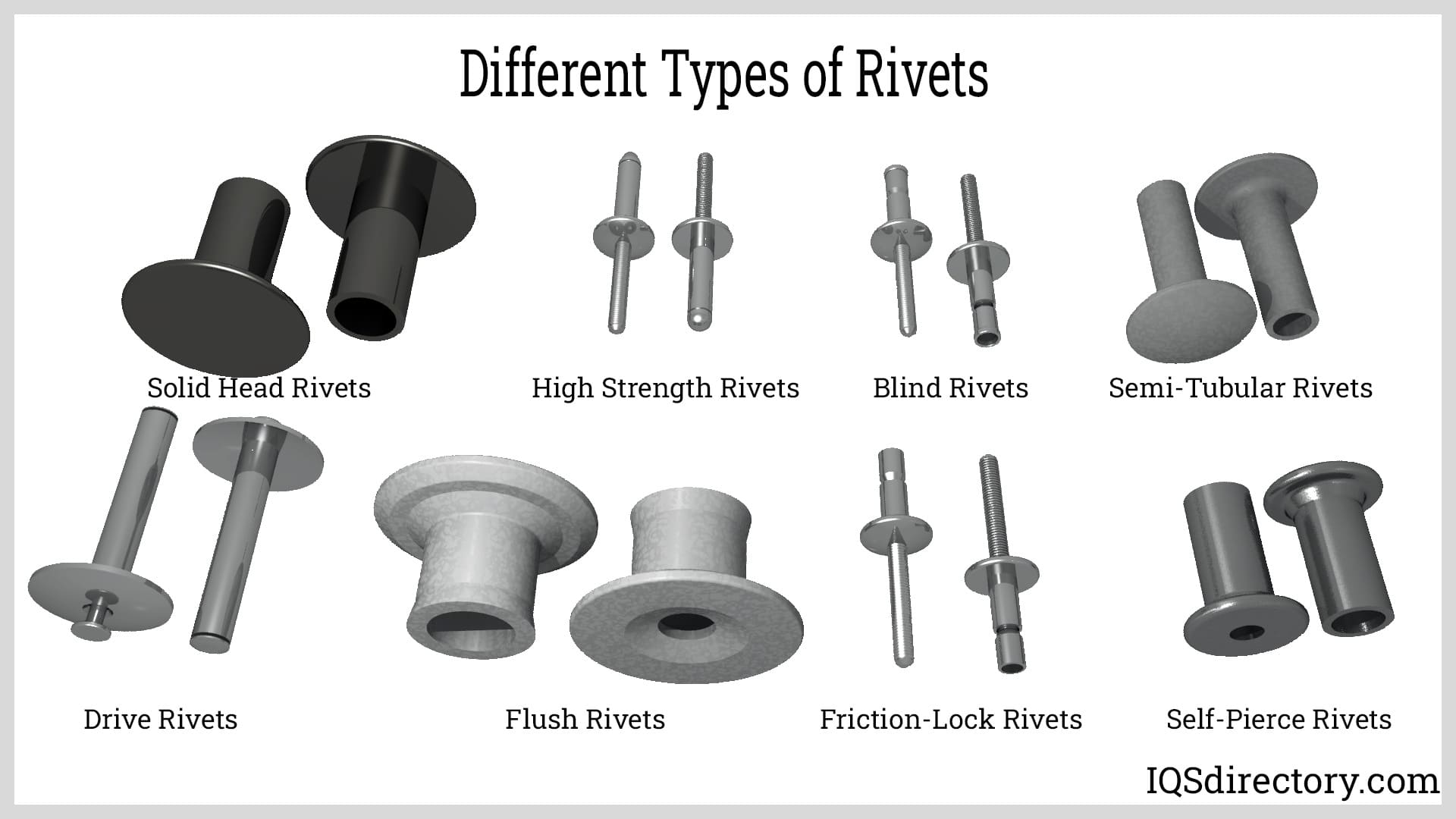
Rivets
Rivets are cylindrical, non-threaded fasteners with a head on one end. They are inserted into pre-drilled holes, and the tail is deformed to create a secure, permanent joint. Riveting is widely used in structural steel, aircraft, bridges, and automotive chassis. Major rivet types include:
- Solid rivets: Offer maximum strength for critical structures.
- Blind rivets (pop rivets): Allow installation from one side of the assembly—ideal for enclosures and sheet metal work.
- Drive rivets: Quickly installed using a hammer for low-load applications.

Interested in high-performance rivets for aerospace, automotive, or industrial manufacturing? Find rivet suppliers and product specifications through our directory.
Permanent Fasteners
Permanent fasteners are designed to create joints that cannot be easily removed without damaging the components or the fastener itself. These are typically used in applications where tamper resistance, vibration resistance, or structural integrity are top priorities.
Nails
Nails are unthreaded fasteners driven by hammer or pneumatic nailer, frequently used in wood construction, framing, and cabinetry. While nails don't provide as much holding power as screws, they offer greater shear strength and faster assembly. Common nail types include:
- Box nails: Diamond-pointed for easy driving into wood and reduced splitting.
- Brad nails: Thin, small-head nails ideal for trim and finish work where concealment is desired.
- Common nails: General-purpose nails for heavy-duty framing and construction.
- Finishing nails: Small head for minimal surface disruption in finish carpentry.

Looking for specialized nails for construction or woodworking? Browse nail suppliers and product specs for your project needs.
Non-Permanent Fasteners
Non-permanent fasteners are designed for disassembly, maintenance, or modularity. These fasteners allow for repeated removal and reinstallation—ideal for machinery, electronics, and products requiring frequent servicing or upgrades.
- Bolts and nuts: The classic combination for strong, reversible joints.
- Clips, snap fasteners, and retaining rings: Allow for quick assembly and disassembly of panels or covers.
- Detent pins and quick-release pins: Used for fast changes or securing moving parts on equipment.
Materials Used in Industrial Fasteners
The choice of fastener material directly impacts performance, reliability, and longevity in various environments. Common materials and their advantages include:
- Steel (carbon and alloy steel): Offers high strength and affordability, with various grades for mechanical requirements.
- Stainless steel: Provides corrosion resistance, making it ideal for food processing, medical, and outdoor applications.
- Brass and copper: Used for electrical conductivity and decorative finishes.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, suitable for aerospace and electronics.
- Titanium: Combines strength, lightness, and chemical resistance for high-performance industries such as aerospace and motorsports.
- Plastic and nylon: Insulating and lightweight for electronics, automotive, and chemical environments.
Are you evaluating which fastener material is best for your operating environment? Consider factors such as load, corrosion, temperature, and chemical exposure when selecting fastener materials.
Applications of Industrial Fasteners
Industrial fasteners are ubiquitous across every sector, each with distinct performance criteria and regulatory requirements. Some major application areas include:
- Automotive and transportation: Fasteners are integral in chassis assembly, engine construction, interior panels, and safety-critical systems. Stringent quality standards and traceability are essential.
- Aerospace and defense: Aircraft, satellites, and military vehicles require lightweight, high-strength fasteners with precise tolerances and certification for airworthiness and safety.
- Construction and infrastructure: Structural steel, bridges, and high-rise buildings rely on heavy-duty bolts, anchors, and weld studs for long-term durability and compliance with building codes.
- Electronics and telecommunications: Miniature screws, nuts, and clips support assembly of devices, circuit boards, and enclosures with requirements for EMI shielding and thermal management.
- Energy and utilities: Power plants, wind turbines, and pipelines use specialized corrosion-resistant fasteners for harsh environments and high mechanical loads.
- Medical devices and healthcare: Biocompatible fasteners are essential for surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment, with requirements for sterilizability and regulatory compliance.
- Consumer goods and appliances: Fasteners in white goods, furniture, and electronics must balance aesthetics, cost, and functionality.
Searching for fasteners for a specific industry or use-case? See fastener solutions by industry to match your project’s demands.
The Importance of Fasteners in Industry
- Efficiency and productivity: The reliability and ease of installation of fasteners directly impact manufacturing and construction efficiency. The right fasteners streamline assembly, reduce production time, and support modular design.
- Durability and longevity: High-quality fasteners ensure structural integrity and extend the service life of equipment, vehicles, and buildings. Inferior fasteners can lead to costly failures and downtime.
- Safety and compliance: Industrial fasteners are critical to safety in high-stakes environments. Failing or substandard fasteners can result in catastrophic accidents, liability, and non-compliance with regulations.
- Maintenance and serviceability: Non-permanent fasteners simplify repairs, upgrades, and regular maintenance, lowering total cost of ownership.
Case Study: In automotive manufacturing, thousands of fasteners are used in each vehicle for frame, engine, interior, and safety systems. Strict quality standards, traceability, and advanced materials (such as high-tensile steel or aluminum alloys) are required to ensure performance, weight reduction, and occupant safety.
Similarly, the aerospace industry relies on certified, high-performance fasteners to withstand vibration, fatigue, and extreme environmental conditions. Each application demands careful selection, testing, and documentation to meet regulatory and operational requirements.
In electronics and consumer products, miniaturized screws and snap fasteners enable compact, repairable designs, supporting both manufacturing efficiency and user-friendly serviceability.
Not all fasteners are used to join metal to metal. Wood screws, for example, are vital for carpentry and furniture making, while specialized fasteners secure plastics, composites, and other non-metallic components in modern manufacturing.
The Benefits of Using Industrial Fasteners
Why choose industrial fasteners over permanent joining methods like welding or adhesives?
- Design flexibility: Fasteners allow for modular construction, easy disassembly, and component replacement. They support a range of design strategies, from lightweighting in vehicles to compact electronics assembly.
- Reduced waste and cost: Fastener-based assembly often requires fewer materials and less labor compared to welding or gluing. This translates to cost savings in materials, tools, and production time.
- Improved aesthetics: Discrete, low-profile fasteners can enhance product appearance and finish.
- Ease of maintenance: Fasteners allow for straightforward repairs and upgrades, reducing downtime and extending product life.
- Standardization and availability: A wide range of fastener sizes, grades, and finishes are readily available from global suppliers, simplifying sourcing and inventory management.
- Performance and reliability: Precision-engineered fasteners meet demanding mechanical, thermal, and environmental criteria for high-performance applications.
Want to learn more about how fasteners can improve your manufacturing process or product design? Explore the advantages of industrial fasteners for your industry.
Key Decision Factors When Choosing Industrial Fasteners
Selecting the right fastener involves balancing technical, economic, and regulatory factors. Consider the following questions when specifying fasteners:
- What loads (tensile, shear, or combined) must the fastener withstand?
- Is the joint permanent or will it require disassembly?
- What are the environmental conditions (temperature, moisture, chemicals, UV exposure)?
- Are there regulatory or industry standards that must be met?
- What materials are being joined (metal, plastic, wood, composites)?
- Is corrosion resistance, conductivity, or insulation required?
- What are the space, weight, and aesthetic constraints?
- What is your required volume, lead time, and sourcing location?
Take the guesswork out of fastener selection—ask our fastener experts for personalized recommendations and technical support.
Selecting the Right Industrial Fastener Manufacturer
Choosing a reliable industrial fastener manufacturer is critical for project success, quality assurance, and supply chain efficiency. When evaluating manufacturers, consider:
- Experience and reputation in your target industry or application
- Range of products, materials, and custom manufacturing capabilities
- Certifications (ISO, ASME, ASTM, etc.) and compliance with industry standards
- Quality control, testing procedures, and traceability systems
- Lead times, minimum order quantities, and logistic support
- Technical support and engineering assistance
- Customer reviews and case studies
For the most constructive outcome when purchasing industrial fasteners, compare several companies using our comprehensive directory of industrial fastener manufacturers. Each manufacturer has a detailed business profile page highlighting their areas of expertise, material range, production processes, certifications, and capabilities. Use our website previewer to quickly assess specializations, and our streamlined RFQ form to contact multiple suppliers for quotes or technical information.
Ready to start your fastener sourcing journey? Request a fastener quote or contact manufacturers directly through our platform to ensure you receive the ideal products for your requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Industrial Fasteners
- What are the most common types of industrial fasteners? Screws, bolts, nuts, rivets, nails, pins, and clips are among the most used fasteners in industrial applications.
- How can I identify the best fastener material for my application? Consider load requirements, corrosion risk, material compatibility, and environmental factors. Consult with suppliers for recommendations based on your use case.
- What standards govern industrial fastener quality? Key standards include ISO, ASTM, ASME, DIN, SAE, and others depending on region and industry.
- Can I order custom fasteners for unique applications? Yes, many manufacturers offer custom fastener design and production services for specialized requirements.
- How do I avoid fastener failures? Use certified, high-quality fasteners matched to your application, follow installation best practices, and perform routine inspections and maintenance.
Conclusion: Maximizing Value with the Right Industrial Fasteners
Industrial fasteners are the backbone of assembly, construction, and manufacturing across the global economy. Selecting the right type, material, and supplier ensures safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness—whether you’re building skyscrapers, assembling vehicles, or manufacturing consumer electronics. With a broad array of fastener options and suppliers available, leveraging expert guidance and advanced sourcing tools will help you achieve optimal results for your project or business.
If you’re ready to streamline your fastener supply chain, optimize product performance, or get expert recommendations, contact our fastener specialists or use our supplier directory to locate the best manufacturers for your needs.








 Bolts
Bolts Fasteners
Fasteners Gas Spring
Gas Spring Handles
Handles Hinges
Hinges Latches
Latches Locks
Locks WIre Hooks
WIre Hooks Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services